The Problem (Overview)
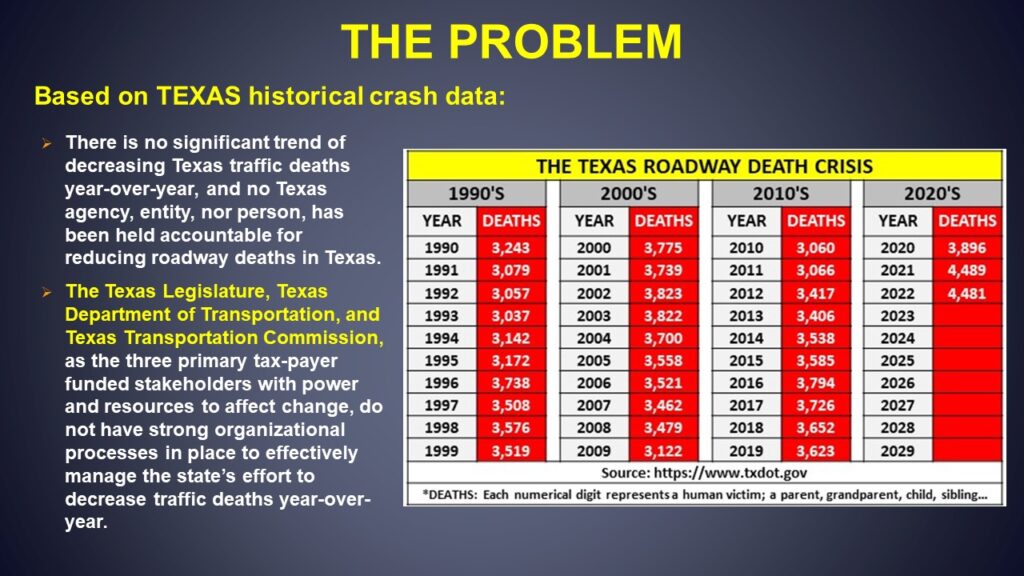
In 2022, there were 4,481 deaths on Texas roadways. For Texas families, that is a tragic and preventable problem. That is, to be forced to endure an unsuspecting roadway death lottery of twelve (12) deaths every day on Texas roadways (on average). To effectively create change to solve a problem, the problem must be fully understood. THE TEXAS TRAFFIC SAFETY PROBLEM: Based on historical crash data, there is no significant trend of decreasing Texas traffic deaths year-over-year, and no Texas agency, entity, nor person has been held accountable for reducing roadway deaths in Texas.
TxDOT, the Texas Transportation Commission, and the Texas Legislature (as the three primary stakeholders with power and resources to affect change) do not have strong organizational processes in place to effectively manage the state’s effort to decrease traffic fatalities year-over-year, primarily because neither entity has identified the ROADWAY DEATH PROBLEM as a crisis and identified the agency, entity, nor person to be held accountable for solving the problem.
The underlying problem causing traffic deaths on Texas roadways cannot be limited to unsafe driver behavior alone. Unsafe roadway design and ineffective/insufficient traffic laws must also be held accountable.
The last year Texas had annual traffic deaths below 3,000 victims was in 1963, sixty years ago. In comparison, California, with about 11 million more people than Texas, had less than 3,000 traffic deaths three consecutive years from 2010 to 2012, and has had fewer traffic deaths than Texas for the past 15 years in a row (2008 – 2022).
Unless you want to argue that California has safer drivers than Texas, the only conclusion must be the California roadway system is better managed (sufficient safe systems or more effective safe systems) to reduce traffic deaths, year-over-year, than the Texas roadway system.
The Problem (Specific Examples)
The Texas Legislature
Problem 1: The State of Texas does not have (nor does it provide annual funds for) a statewide commission that has the sole purpose and resources to reduce Texas traffic fatalities and serious injuries year-over-year. Without this commission and its distinct job description, responsibility, and performance measures, the Texas Legislature and other State organizations are not held accountable for public safety on Texas roadways. An example of this type of commission is the Washington Traffic Safety Commission (for information, click on link), which is chaired by Washington’s Governor Jay Inslee and is made up of ten Commissioners representing the four E’s of traffic safety (Education, Enforcement, Engineering, and Emergency Medical Services).

Problem 2a: The Texas Legislative process has not passed sufficient or effective traffic safety laws that has effectively reduced traffic fatalities and serious injuries on Texas roadways year-over-year.
- For DWI laws, reduce the Blood Alcohol Concentration limit from 0.08 to 0.05%BAC
- For Distracted Driving laws, a statewide hands-free law with no loopholes that allows typing data into hand-held devices, while driving, for Navigation or Music Apps
- For Speed Limit laws, a ban on the use of the 85th Percentile Rule for setting speed limits and a transition to a safer method of using USLIMITS2.
- For Speed Limit laws, a ban on TxDOT implementing 70-75 mph speed limits on undivided roadways to eliminate the increased blunt force trauma of 33% on Texas crash victims (no other State allows 70-75 mph speed limits on undivided roadways, only Texas Legislators allow such a deadly speed on the most deadly roadway design, the undivided roadway).
- For Speed Limit laws, using national peer-reviewed data on the (reduced) effectiveness of seat belts and/or airbags if speed limits are increased and its effect on public safety
Problem 2b: The Texas Legislative process has banned traffic safety devices or voted down laws that were recommended by the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), the National Safety Council (NSC), the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) Strategic Highway Safety Plan, or other nationally recognized traffic safety organizations.
- Red Light Cameras
- Automated Speed Enforcement Devices
- Governor’s veto of HB448 requiring drivers to use rear-facing car seats for children under 2-years of age, child weight and height restrictions apply (June 2019)
The Texas Department of Transportation
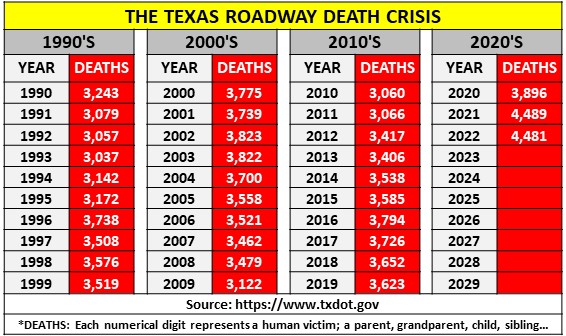
Problem 1: TxDOT does not have a Safety Division with a Chief Safety Officer that has an equal seat-at-the-table as other division chiefs. TxDOT does not have a Chief Safety Officer that is held responsible, and that has the job description, stated mission, or performance measures to effectively reduce traffic fatalities and serious injuries year-over-year. TxDOT does not provide annual funding (that is guaranteed and recurring) to a Safety Division to ensure success in its mission to effectively reduce traffic fatalities and serious injuries year-over-year.
Problem 2: TxDOT does not enhance its organizational safety culture with a mission statement that mentions the word “safety,” nor mentions its primary mission of public safety.
Problem 3: TxDOT has policies, practices, and speed limits that likely create hazards to road-users that other road-users in other States do not have to endure. These hazards may create a higher risk to the safety and well-being of road-users (injury and/or death) and may increase the risks associated with property/vehicle damage. These hazards are listed below and mostly involve drivers NOT having a sufficient clear zone to allow the vehicle to safely return to the desired roadway or to stop in a safe area after experiencing human error that caused the vehicle to initially vacate the desire roadway (travel lane). First, for better understanding of the “Clear Zone” hazards, here is the definition of Clear Zone.
Clear Zone: The total roadside area, starting at the edge of the traveled way, available to errant (off-the-roadway) vehicle drivers to safely bring their vehicle to a safe stop or safely return to the roadway, without crashing into any object, vehicles traveling in the opposite direction, or rolling-over due to steep engineered roadside slopes. This area may consist of a opposite direction travel lane, shoulder, a recoverable slope (driver is able to safely stop or safely return to the roadway), a non-recoverable slope (driver stops safely at the bottom of the slope and is not able to return to the roadway), and/or a clear run-out area (paraphrased from www.fhwa.dot.gov, click on the link for more information).
TxDOT Definition of Clear Zone: The unobstructed, traversable area provided beyond the edge of the through traveled way for the recovery of errant vehicles. The clear zone includes shoulders, bike lanes, and auxiliary lanes, except those auxiliary lanes that function like through lanes (Source: https://ftp.dot.state.tx.us/pub/txdot-info/des/guides/roadside-safety.pdf, Pg 6, Glossary).
- Hazard 1: TxDOT’s Use of the 85th Percentile Rule for Setting Speed Limits and the Rule’s Total Disregard for Human Survivability During Traffic Crashes. TxDOT’s disregard to incorporate the NTSB’s recommendation to transition away from solely using the 85th Percentile Rule to using the method of USLIMITS2 for setting safe speed limits.
- Hazard 2: TxDOT’s Increased Speed Limits on Undivided Roadways (Opposite-Direction Vehicles in the Clear Zone and its Affect on Human Survivability During Centerline-Crossing, Head-On Vehicle Crashes and Intersection T-bone Crashes).
- Hazard 3: TxDOT’s Increased Speed Limits and Its Affect on Human Survivability in Relation to the Effectiveness of Seat Belts, Airbags, and Vehicle Structural Integrity During Vehicle Crashes.
- Hazard 4: TxDOT’s High-Speed Limit (65-75mph) Work Zones; 1) Allowing high-speed traffic to flow within feet of unprotected construction workers (workers NOT protected with hardened barriers between traffic and themselves), and 2) placing guardrail crash attenuators within inches of high-speed traffic without mitigation of a A) slower regulatory speed limit in the work zone or B) engineering a flared guardrail system with crash attenuators 10 or more feet from the roadway (see Hazard 6, below).
- Hazard 5: TxDOT’s Disregard of Clear Zone Principles.
- Hazard 6: TxDOT’s Guardrails in the Clear Zone, inches from the roadway.
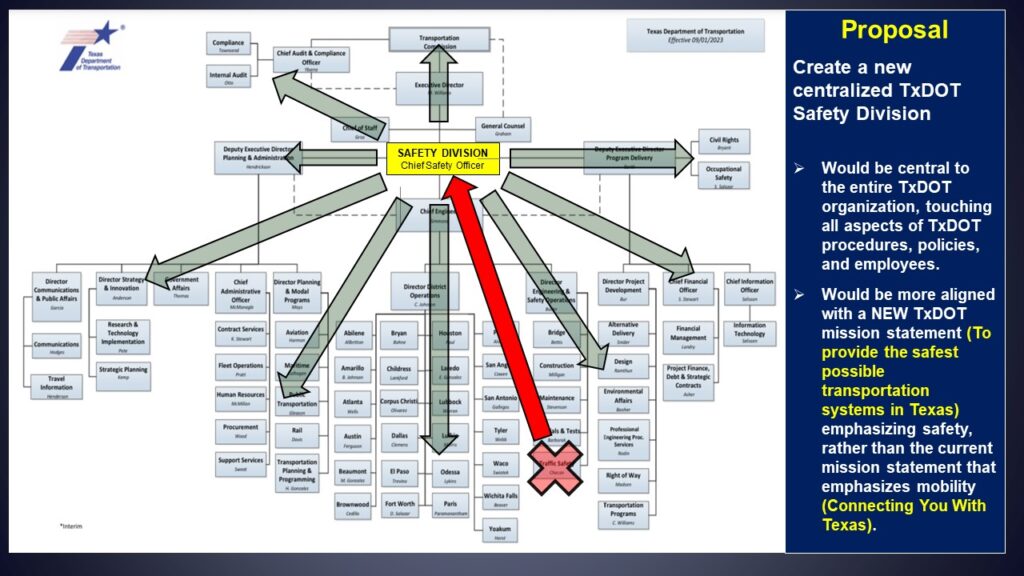
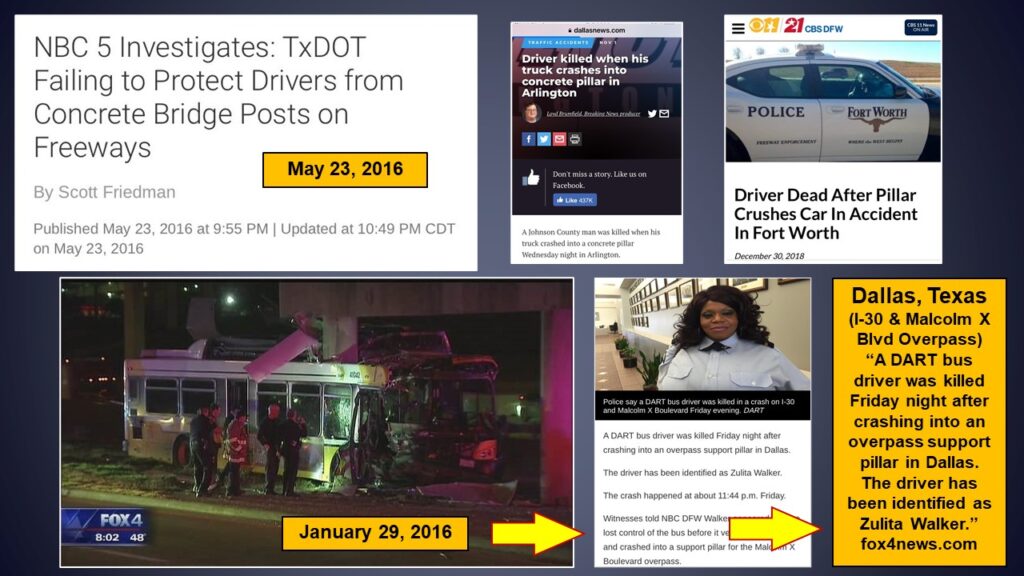
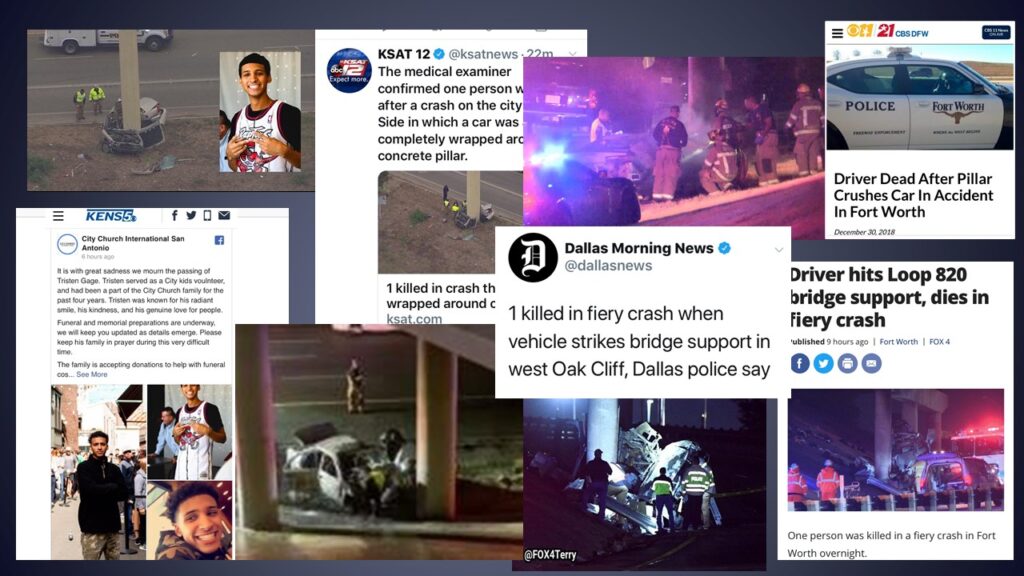
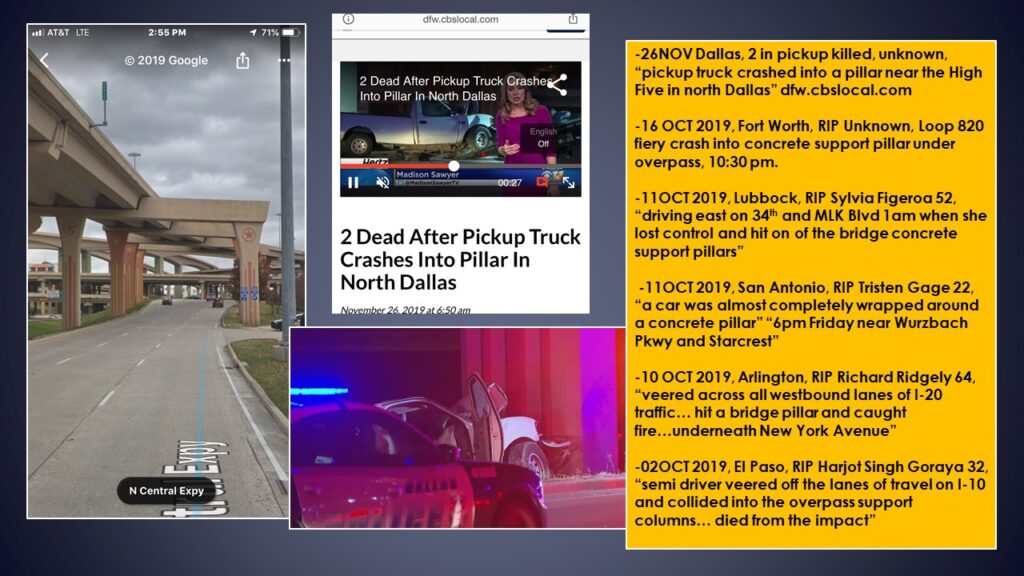
- Hazard 7: TxDOT’s Concrete Support Pillars in the Clear Zone.
- Hazard 8: TxDOT’s Utility Poles, Culverts, Trees (& Other) in the Clear Zone.
- Hazard 9: TxDOT’s Ineffective Protection of Median Drop-Offs in the Clear Zone at Overpasses and Bridges.
- Hazard 10: TxDOT’s Placement of Median Cable Guardrails in the Clear Zone.
- Hazard 11: TxDOT’s Unsafe Speed Management in Work Zones.
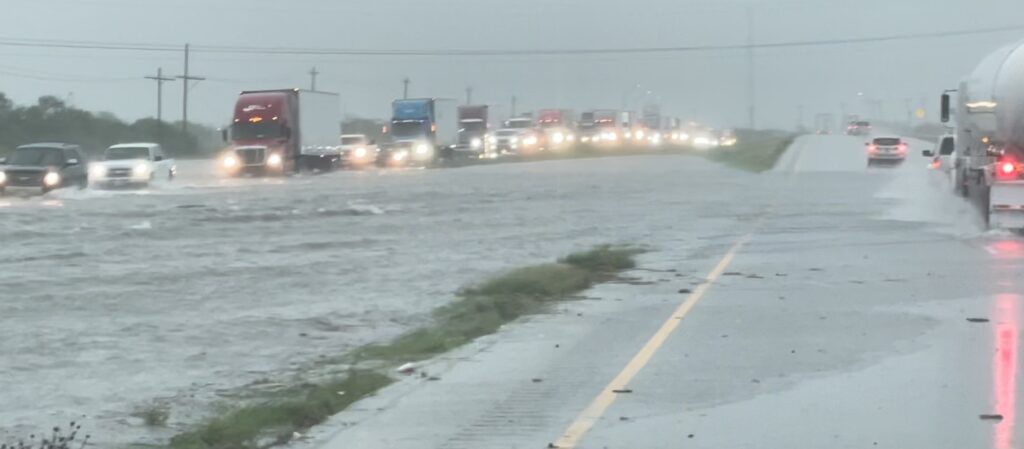
- Hazard 12: TxDOT’s Roadway Flood/Drainage Management and the TxDOT System that Allows or Does Not Allow Vehicle Drivers Entry or Access to Flooded Roadways.
- Hazard 13: TxDOT’s Use of “Traffic Volume” in Determining Clear Zone Distances (Reduces Safety Margins for Those Drivers on Less Traveled Roadways, Like Farmers or other Rural Roadway-Users).
- Hazard 14: TxDOT’s Use of “Linear” Distances of Fixed-Objects from the Roadway in Relation to “Exponential” Vehicle Speed in Determining Clear Zone Distances (Using the Kinetic Energy Formula in Relation to Vehicle Stop/Brake Distances During Vehicle Crashes).
TxDOT’s 70-75mph Speed-Limit on Undivided Roadways (using the 85th Percentile Rule)





TxDOT’s Unethical and Deadly 70-75mph Speed-Limit Work Zones
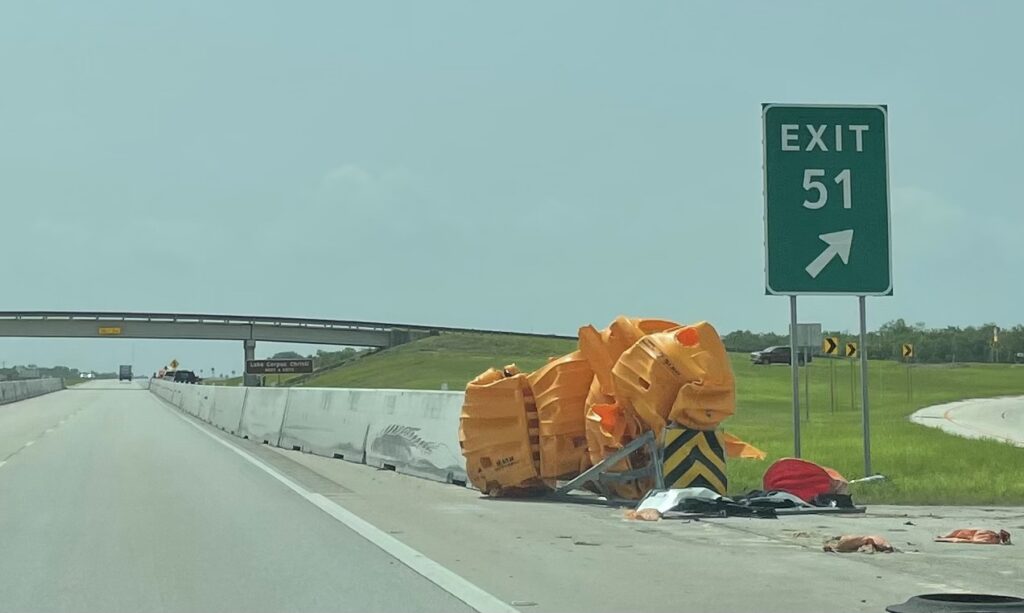















TxDOT Guardrails




TxDOT Concrete Support Pillars
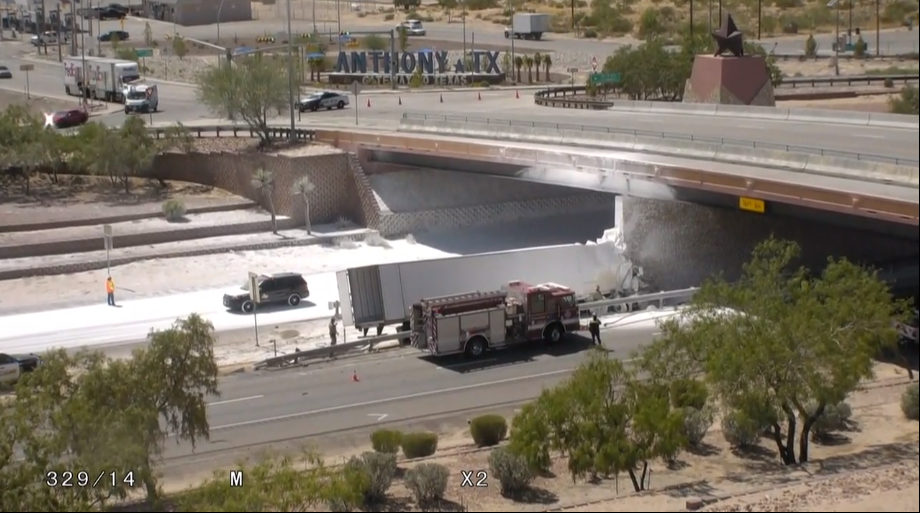
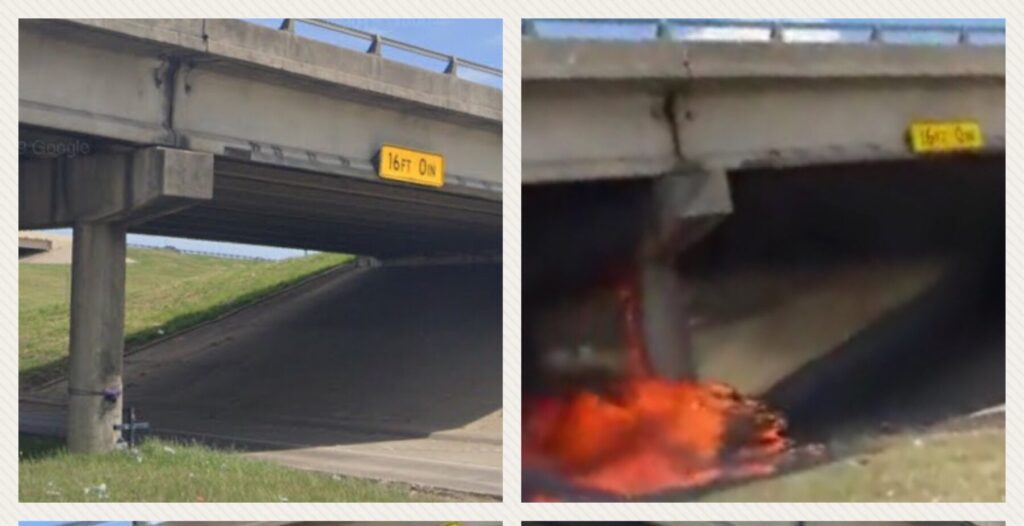



Trees in the Clear Zone



SUCCESS! Here’s a TxDOT photo (04OCT2022) after the trees near Faysville, Texas, were removed after Vision Zero South Texas submitted an online complaint about the deadly trees being only 15 feet from a roadway with a 75mph speed limit (Case Number 279526, 23MAY2022).
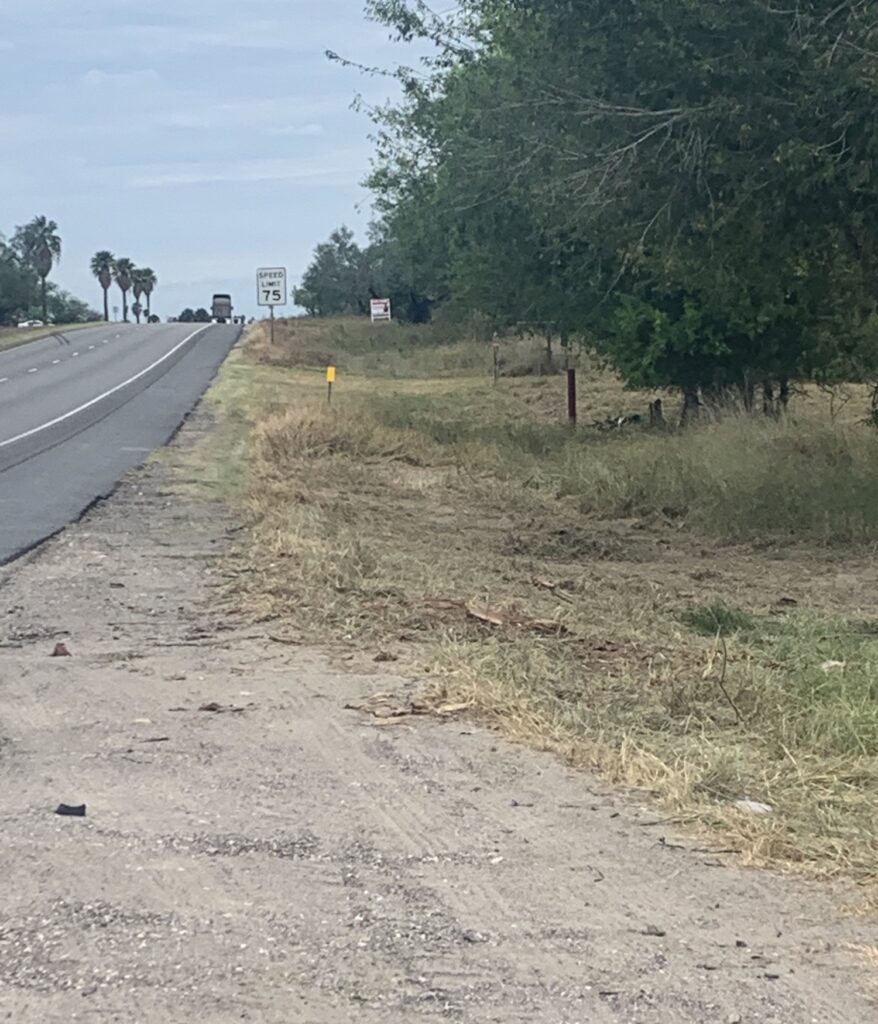


SUCCESS! Here’s a TxDOT photo (04OCT2022) after the deadly tree near Linn, Texas, was removed after Vision Zero South Texas submitted an online complaint about the tree being only 16 feet from a roadway with a 75mph speed limit (Case Number 280117, 17JUN2022).

TxDOT Median Drop-Offs

TxDOT Flood Management



Sorry, this page is under construction.
